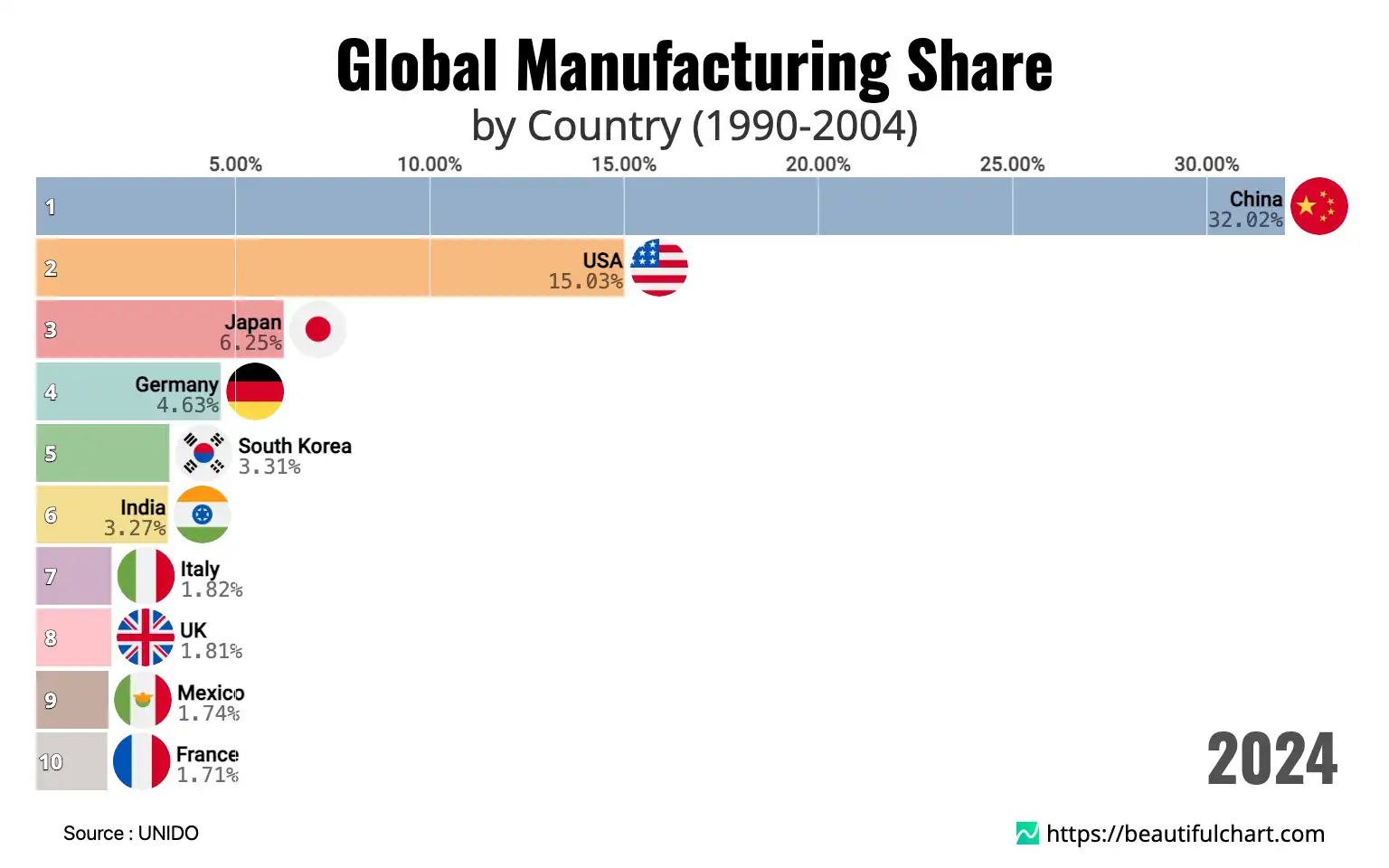
The global manufacturing landscape is dominated by China, which accounts for 32.02% of the world's total output. The United States holds the second position with a 15.03% share, highlighting a significant gap between the top two industrial powers. Following them are Japan and Germany, with 6.25% and 4.63% respectively, indicating a concentration of manufacturing power among a few key nations.
Manufacturing output refers to the total value of goods produced by a country's industrial sector within a specific period. It is a critical indicator of economic health and industrial capacity, reflecting a nation's ability to convert raw materials into finished products for domestic consumption or export.
A profound transformation has reshaped the world's industrial landscape over the past three decades. The distribution of production capabilities has shifted dramatically, moving away from the traditional powerhouses of the 20th century and toward new centers of industrial might. This evolution reflects broader economic, technological, and geopolitical trends that have redefined global commerce and supply chains.
The Unprecedented Rise of a Manufacturing Superpower
The most significant development has been the ascendancy of China as the world's factory. Beginning from a modest 3.15% share in 1991, its growth has been relentless. By the early 2000s, it had surpassed Germany and Japan, and by 2009, it was nearly equal with the United States. Today, it commands nearly a third of the world's total manufacturing output. This meteoric rise was fueled by a combination of factors, including massive state-led investment in infrastructure, a vast and disciplined labor force, and policies designed to attract foreign investment and technology transfer. The nation became an indispensable hub for global supply chains, producing everything from consumer electronics and textiles to heavy industrial equipment. Its scale of production has allowed it to influence global prices and set new benchmarks for industrial capacity.
The Shifting Role of Traditional Industrial Leaders
While China's expansion has been the defining story, the roles of established industrial leaders like the United States and Japan have evolved. The United States, which held the top position for decades with a share consistently above 20%, has seen its proportion decline to 15.03%. However, this figure does not tell the whole story. The U.S. has pivoted toward higher-value and technologically advanced sectors, such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, and software-integrated hardware. It remains a global leader in innovation and research and development, maintaining a competitive edge in capital-intensive and high-skill industries. Japan's trajectory shows a more pronounced decline, with its share falling from over 14% in 1991 to 6.25%. Once a peerless leader in automotive and electronics, it has faced stiff competition and a prolonged period of economic stagnation. Germany has remained a resilient European powerhouse, maintaining a relatively stable, albeit slowly declining, share. Its strength lies in high-quality engineering, premium automobiles, and specialized industrial machinery, allowing it to retain a strong position in the top tier.
The Emergence of New Industrial Centers
Beyond the top players, the data reveals the rise of other significant industrial economies. South Korea has firmly established itself as a top-five manufacturing nation, driven by its global leadership in semiconductors, electronics, and shipbuilding. Its journey from 1.75% in 1991 to 3.31% today showcases a successful strategy based on innovation and export-oriented growth. India has also emerged as a major player, climbing into the top ranks with a focus on pharmaceuticals, automotive components, and chemicals. Other nations like Mexico, Indonesia, and Turkey have also expanded their industrial bases, reflecting a broader trend of diversification in global production away from a handful of countries. This diffusion of industrial capability is creating a more complex and multi-polar global economic system.
Key Takeaways
China's Manufacturing Ascendancy
- China leads the world with a 32.02% share of global manufacturing output.
- Its share has grown more than tenfold since 1991, when it was just 3.15%.
- There is a significant 17-percentage-point gap between China and the second-place United States.
Evolution of Established Powers
- The United States' share has decreased from over 21% in the early 1990s to 15.03%, but it remains a leader in high-tech sectors.
- Japan's share has more than halved, falling from over 14% to 6.25%.
- Germany has maintained its position as a top European industrial nation, focusing on high-value engineering.
Rise of New Industrial Centers
- South Korea has entered the top five, with its share growing from 1.75% to 3.31%.
- India has also become a top-tier manufacturing country, now ranked sixth globally.
- Nations like Mexico, Indonesia, and Turkey have significantly expanded their industrial capabilities.
Top Ranking
#1 China 32.02%
China stands as the undisputed leader in global manufacturing, contributing nearly a third of the world's total output. Its journey from a minor player in the early 1990s to the world's factory is a story of unprecedented industrialization. This dominance is built on massive economies of scale, a comprehensive industrial ecosystem, and significant government investment in technology and infrastructure. China is a critical link in countless global supply chains, producing a vast range of goods from consumer electronics and textiles to advanced telecommunications equipment and renewable energy technology.
#2 USA 15.03%
The United States holds the second position, demonstrating its continued strength as a major industrial power. While its overall share has declined from its 20th-century peak, the U.S. has successfully transitioned towards high-value, technology-intensive manufacturing. It remains a global leader in key sectors such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, semiconductor design, and medical devices. The nation's industrial output is characterized by a strong emphasis on innovation, research and development, and a highly skilled workforce, which sustains its competitiveness in the most advanced and profitable segments of the global market.
#3 Japan 6.25%
Japan ranks third, maintaining its reputation for high-quality, precision manufacturing. Although its global share has contracted amid rising competition, the country remains a powerhouse in the automotive and electronics industries. Japanese companies are renowned for their technological sophistication, particularly in robotics, specialized components, and advanced materials. The nation's industrial philosophy, focused on efficiency and continuous improvement, allows it to command a premium in global markets and maintain a crucial role in high-tech supply chains.
#4 Germany 4.63%
As the leading manufacturing nation in Europe, Germany secures the fourth spot globally. Its industrial strength is rooted in its 'Mittelstand'—a network of small and medium-sized enterprises that are often world leaders in niche markets. Germany excels in producing complex industrial machinery, luxury automobiles, and high-quality chemicals. The brand 'Made in Germany' continues to be synonymous with engineering excellence, reliability, and innovation, allowing the country to sustain a strong, export-oriented industrial base despite global shifts.
#5 South Korea 3.31%
South Korea's entry into the top five highlights its remarkable economic development over the past few decades. Its manufacturing sector is a global force, driven by world-leading conglomerates in electronics, semiconductors, and shipbuilding. South Korea has successfully leveraged a strategy of aggressive investment in research and development and export-oriented policies to build a technologically advanced and highly competitive industrial economy. Its leadership in memory chips and display technology makes it an indispensable player in the global electronics industry.
| Rank | Name | Indicator |
|---|---|---|
1 | 32.02% | |
2 | 15.03% | |
3 | 6.25% | |
4 | 4.63% | |
5 | 3.31% | |
6 | 3.27% | |
7 | 1.82% | |
8 | 1.81% | |
9 | 1.74% | |
10 | 1.71% | |
11 | 1.63% | |
12 | 1.56% | |
13 | 1.39% | |
14 | 1.33% | |
15 | 1.17% | |
16 | 1.07% | |
17 | 1.04% | |
18 | 1.03% | |
19 | 0.99% | |
20 | 0.74% |