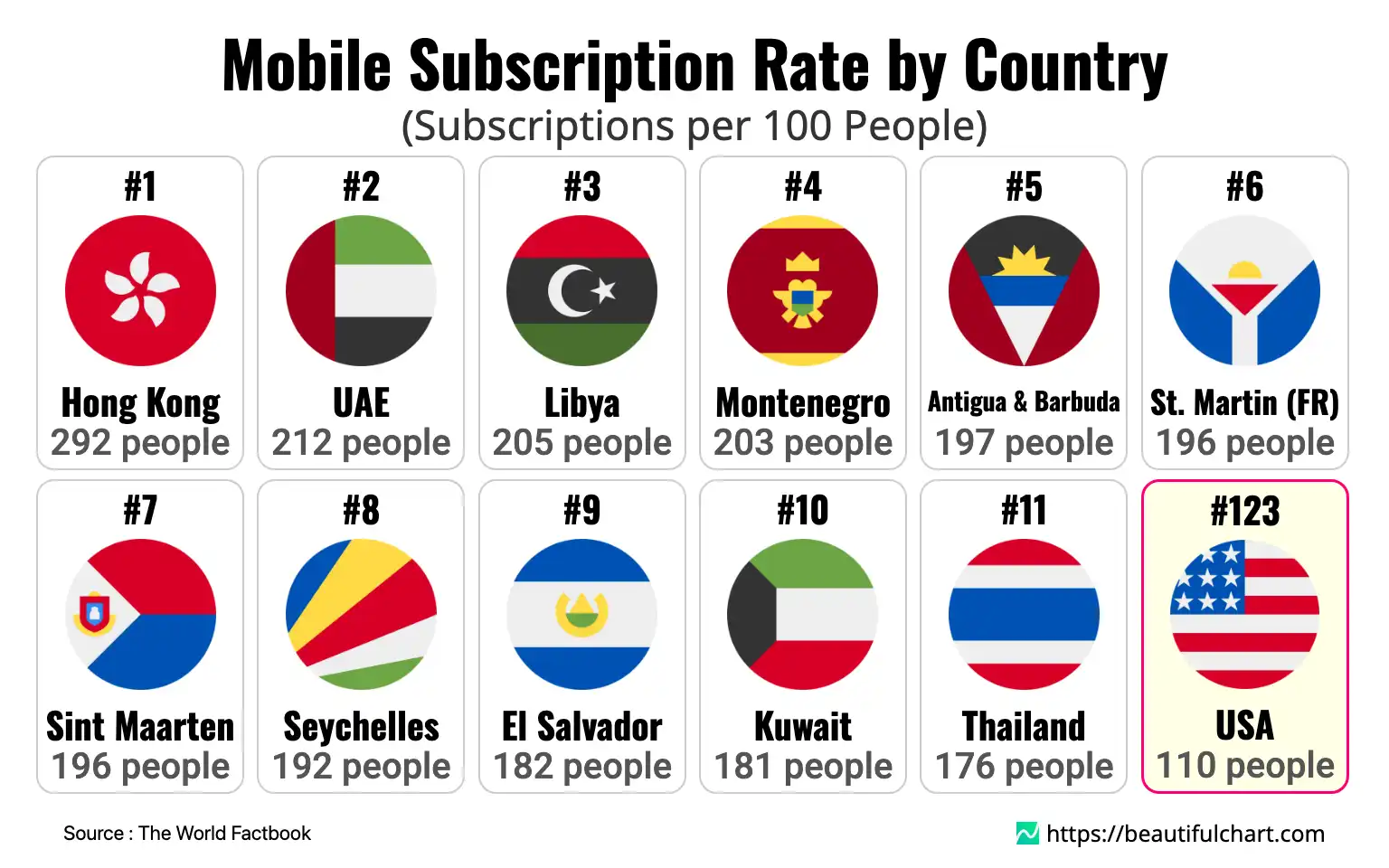
The global landscape of mobile connectivity reveals that numerous countries have more mobile subscriptions than inhabitants. Hong Kong leads with an astonishing 292 subscriptions per 100 people, followed closely by the UAE. This trend highlights a world where individuals often manage multiple devices or SIM cards for personal and professional use. In contrast, the United States has 110 subscriptions per 100 people, indicating a mature but less saturated market compared to the global frontrunners.
Mobile Penetration Rate refers to the number of active mobile phone subscriptions within a specific population, typically calculated per 100 inhabitants. A rate exceeding 100 indicates that there are more subscriptions than people, a common scenario due to individuals owning multiple devices or SIM cards.
The distribution of mobile cellular subscriptions per 100 people reveals significant insights into global economic development, technological infrastructure, and societal behaviors. The data indicates a widespread phenomenon where the number of subscriptions surpasses the population in many nations, a condition known as market over-saturation. This is not an anomaly but rather a reflection of modern communication habits, where individuals may possess multiple SIM cards for different purposes, such as personal use, work, or international travel. Furthermore, the proliferation of data-only devices, including tablets, mobile hotspots, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, contributes substantially to these figures.
Drivers of High Mobile Penetration
Several factors contribute to the high penetration rates observed in top-ranking territories like Hong Kong and the UAE. These locations are often global financial hubs and centers for international business, where staying connected is paramount. Professionals and expatriates frequently maintain both a local and a home country number, driving up subscription counts. Additionally, competitive telecommunications markets in these areas often lead to affordable and attractive data plans, encouraging consumers to own multiple subscriptions. Tourism also plays a vital role in smaller nations or islands like Antigua & Barbuda, where the influx of visitors purchasing temporary local SIM cards artificially inflates the subscription-to-population ratio.
The Socio-Economic Spectrum of Connectivity
The figures paint a picture of a stark digital divide. While many developed and emerging economies show penetration rates well over 100%, numerous developing countries in Africa and parts of Asia lag significantly. Nations like South Sudan and North Korea have rates below 30 subscriptions per 100 people, reflecting challenges related to infrastructure, affordability, and political restrictions. In these regions, access to mobile technology is not just a matter of convenience but a critical component of economic and social development, enabling access to financial services, education, and healthcare information. The United States, with 110 subscriptions per 100 people, represents a mature market. While its rate is high, it is surpassed by many other nations, which can be attributed to a market structure that often favors family plans and single-provider solutions over the multi-SIM culture prevalent in many parts of Europe and Asia.
Future Trends and Implications
The ongoing global rollout of 5G technology is expected to further influence these numbers. The new generation of wireless technology will power an explosion in connected IoT devices, from smart home appliances to autonomous vehicles and industrial sensors. This will likely push subscription figures even higher in technologically advanced countries. Conversely, for nations at the lower end of the spectrum, the primary challenge remains the expansion of basic, reliable mobile infrastructure. Closing this connectivity gap is essential for fostering inclusive growth and ensuring that all populations can participate in the increasingly digital global economy. The data underscores that mobile connectivity is a complex indicator influenced by a confluence of economic strength, technological advancement, market dynamics, and demographic factors.
Key Takeaways
Market Saturation and Multi-Device Culture
- Many countries exhibit a mobile penetration rate exceeding 100%, indicating that the number of active subscriptions is greater than the population. This highlights a global trend of individuals using multiple devices, such as for personal and work purposes.
- The high subscription rates in places like Hong Kong and the UAE are driven by their status as international business hubs, where professionals and travelers often use multiple SIM cards.
- The proliferation of data-only devices, including tablets, wearables, and Internet of Things (IoT) technology, is a significant contributor to the over-saturation of mobile markets.
The Global Digital Divide
- The data reveals a stark contrast in mobile access between highly developed nations and those with emerging or struggling economies. While top-ranked countries boast rates over 200%, the least connected nations fall below 30 subscriptions per 100 people.
- Economic factors, the state of telecommunications infrastructure, and government policies are primary determinants of a country's mobile penetration rate.
- For many developing nations, increasing mobile access is a critical priority for economic growth, financial inclusion, and improved access to essential services like education and healthcare.
Top Ranking
#1 Hong Kong: 292 people
Hong Kong's status as a global financial center and a densely populated urban environment are key drivers of its world-leading mobile penetration rate. Business professionals, expatriates, and frequent travelers often maintain multiple SIM cards for local and international communication, significantly boosting subscription numbers. The highly competitive telecommunications market offers a wide array of affordable and data-rich plans, encouraging consumers to have separate subscriptions for different devices like smartphones, tablets, and mobile hotspots. Furthermore, its advanced and ubiquitous 4G and 5G infrastructure makes seamless multi-device connectivity a part of daily life for its residents.
#2 UAE: 212 people
The United Arab Emirates' high mobile penetration rate is a reflection of its affluent, tech-savvy population and its position as a major hub for international business and tourism. The country has a large expatriate community, many of whom hold both a personal and a work-provided mobile line, as well as SIMs from their home countries. The government's strong focus on digital transformation and smart city initiatives has led to world-class mobile infrastructure. This environment, combined with high disposable incomes, fosters a culture of early technology adoption and ownership of multiple connected devices per person.
#3 Libya: 205 people
Libya's high mobile subscription rate can be seen as a unique consequence of its post-conflict environment and economic structure. In a country where fixed-line infrastructure may be unreliable or damaged, mobile phones have become the primary and most dependable means of communication for the vast majority of the population. Citizens often purchase multiple SIM cards from competing providers to take advantage of promotional offers or to ensure network coverage in different regions. This reliance on mobile technology for both personal and business activities has driven the subscription count well above the actual population number.
#4 Montenegro: 203 people
As a popular European tourist destination, Montenegro's mobile penetration rate is significantly influenced by the seasonal influx of visitors. Tourists frequently purchase local prepaid SIM cards for affordable data and calls during their stay, which temporarily inflates the number of active subscriptions relative to its small resident population. Additionally, the competitive landscape among mobile operators encourages residents to own multiple SIMs to leverage different network deals and coverage advantages. This combination of a robust tourism sector and competitive local market dynamics pushes its subscription rate to one of the highest in the world.
#5 Antigua & Barbuda: 197 people
Similar to other small island nations with a heavy reliance on tourism, Antigua & Barbuda's high mobile subscription rate is largely driven by the constant flow of international visitors. The tourism industry, which is the cornerstone of its economy, brings a large number of people who purchase local SIM cards for connectivity during their vacation. This seasonal demand, layered on top of the resident population's own mobile usage, results in a subscription figure that is nearly double the number of its inhabitants. The need for reliable communication for both tourists and service providers in the hospitality sector underpins this high penetration rate.
#123 USA: 110 people
The United States has a mobile penetration rate of 110 subscriptions per 100 people, indicating a mature and saturated market. While the rate is above 100%, it is lower than that of many other developed nations. This is partly due to the market structure, which is dominated by postpaid plans, often including family packages that consolidate multiple lines under a single account rather than separate prepaid SIMs. While multi-device ownership is common, the consumer habit of juggling multiple providers is less prevalent than in many Asian and European countries. The nation's vast and diverse geography also presents unique challenges for achieving the ubiquitous, high-density coverage seen in smaller, more compact nations.
| Rank | Name | Indicator | Subindicator |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | 292 people | Total - 23,800,000 | |
2 | 212 people | Total - 21,200,000 | |
3 | 205 people | Total - 13,900,000 | |
4 | 203 people | Total - 1,310,000 | |
5 | 197 people | Total - 184,000 | |
6 | 196 people | Total - 68,840 | |
6 | 196 people | Total - 68,840 | |
8 | 192 people | Total - 165,000 | |
9 | 182 people | Total - 11,500,000 | |
10 | 181 people | Total - 8,109,999 | |
11 | 176 people | Total - 121,000,000 | |
12 | 175 people | Total - 1,370,000 | |
13 | 174 people | Total - 53,600,000 | |
13 | 174 people | Total - 4,700,000 | |
15 | 170 people | Total - 26,000 | |
16 | 169 people | Total - 245,000,000 | |
17 | 168 people | Total - 219,000,000 | |
18 | 167 people | Total - 108,000,000 | |
19 | 165 people | Total - 4,440,000 | |
19 | 165 people | Total - 151,000,000 |