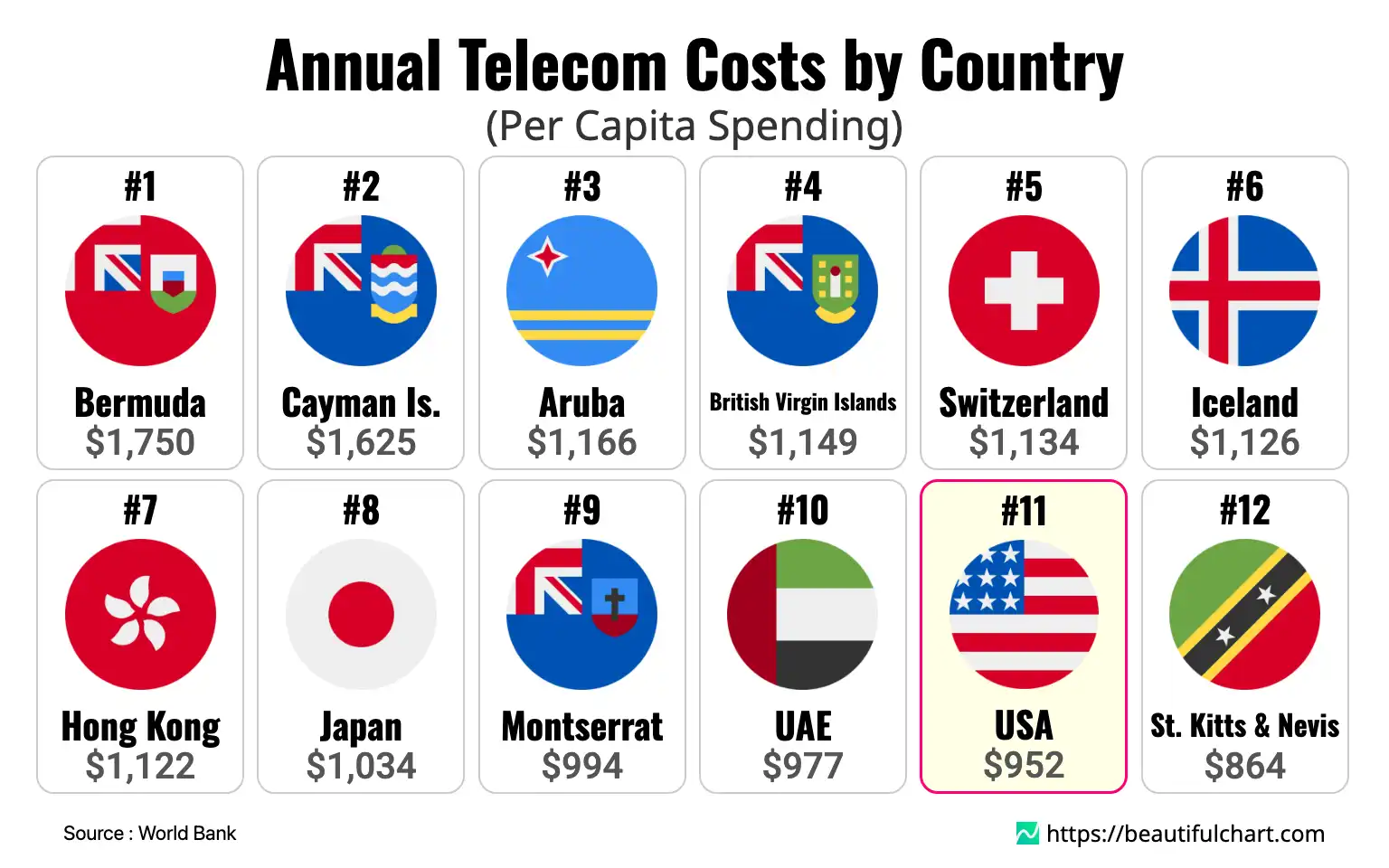
Global per capita communication expenditures exhibit significant disparities across nations. High-income island economies like Bermuda and the Cayman Islands lead in annual spending, with developed countries such as Switzerland also featuring prominently. The United States ranks within the top tier, reflecting diverse market conditions influencing telecom costs globally.
Per Capita Communication Costs refer to the average annual amount an individual spends on telecommunication services, including mobile, internet, and fixed-line services. This metric provides insight into consumer spending habits and the overall cost of connectivity within a country's economy.
Telecommunication services have become an indispensable part of modern life, facilitating everything from basic communication to complex global commerce. The financial outlay an individual incurs for these services annually, when viewed on a per capita basis across different countries, reveals a fascinating and often stark global landscape of connectivity costs.
At the forefront of this expenditure are typically small island nations and territories. These regions often face unique challenges that drive up the cost of telecommunications. Their small population bases mean that the significant fixed costs associated with building and maintaining advanced communication infrastructure, such as undersea fiber optic cables or satellite links, are distributed among a much smaller pool of subscribers. This lack of economies of scale, coupled with a reliance on imported technology and skilled labor, contributes to higher operational expenses. Furthermore, limited land area and geographical isolation can make infrastructure deployment more complex and costly. In many cases, these territories also host affluent populations or act as financial hubs, where a demand for premium, high-speed, and reliable services can justify higher price points.
Beyond these specialized island economies, developed nations also show substantial per capita spending. Countries like Switzerland, Japan, and the United States demonstrate high annual outlays, but for somewhat different reasons. These nations typically possess highly advanced and extensive telecommunication networks, featuring widespread fiber-optic broadband and cutting-edge mobile technologies. The higher disposable income of their populations enables greater consumption of data-intensive services, subscription to multiple communication platforms, and the adoption of the latest devices. Consumers in these markets often prioritize speed, reliability, and value-added services, which can command higher prices. The robust competition in some of these markets, while generally beneficial for consumers, still involves significant investment by providers in network upgrades, spectrum acquisition, and customer service, all of which contribute to the overall cost structure.
Conversely, countries with lower per capita spending often grapple with challenges related to economic development, infrastructure access, and affordability. In many developing nations, lower average incomes mean that telecom services must be priced very low to be accessible to the general populace. This often translates to less sophisticated infrastructure, with more reliance on older mobile technologies or limited broadband penetration, especially in rural areas. The focus in these markets might be more on basic voice and text services rather than high-speed internet. While efforts are often made to expand digital inclusion, the economic realities can limit investment in the most advanced networks, impacting both service quality and the potential for increased spending.
The variations in per capita communication costs are not merely statistical curiosities; they have profound implications for economic development and the global digital divide. Affordable and reliable access to telecommunication services is critical for education, healthcare, e-commerce, and overall economic productivity. High costs can create barriers to entry for businesses, limit access to information for individuals, and hinder a country's ability to participate fully in the global digital economy. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide face the ongoing challenge of balancing the need to foster competition, encourage infrastructure investment, ensure network security, and make services affordable and accessible to all citizens. The patterns of spending reflect a complex interplay of geography, economic development, market structure, consumer demand, and regulatory frameworks.
Key Takeaways
Global Disparities in Spending
- There is an extreme range in annual per capita communication expenditures worldwide, indicating vast differences in access and affordability.
- Small island nations and wealthy economies consistently dominate the top ranks in per capita spending, reflecting unique market and geographical influences.
- Connectivity represents a significant annual household expense in many high-income regions, underscoring its importance in modern daily life.
Factors Influencing High Expenditures
- Market size, the sophistication of infrastructure, and the level of competition play pivotal roles in determining communication costs.
- High-income countries often afford better and more advanced services, driving up individual spending due to demand for premium features and high data usage.
- Geographical constraints, particularly for island nations, can significantly increase the cost of infrastructure development and maintenance, passed on to consumers.
Top Ranking
1st Bermuda $1749.7
Bermuda, a small island territory and a prominent offshore financial center, leads globally in per capita communication costs. This high expenditure can be attributed to several factors typical of island economies, including the high cost of importing technology, limited economies of scale due to a small population, and the necessity of robust, reliable infrastructure to support its high-income residents and demanding business sector. The geographically isolated nature also often necessitates expensive submarine cable connections, contributing to elevated service prices.
2nd Cayman Is. $1625.4
The Cayman Islands, another major global financial hub and luxury tourist destination, follows closely behind Bermuda. Similar to other high-spending island nations, its communication costs are driven by the need for advanced, highly reliable telecommunications infrastructure to serve its affluent resident population and international business operations. The small market size means higher fixed costs per user, alongside the expense of maintaining sophisticated networks in a geographically constrained environment and importing essential equipment and expertise.
3rd Aruba $1166.4
Aruba, a popular Caribbean tourist destination, ranks third for annual per capita communication spending. The demand for seamless connectivity from both its local population and a significant influx of tourists drives substantial investment in its telecom infrastructure. As an island nation, Aruba faces the inherent challenges of high infrastructure costs due to geographical isolation and dependence on imported technology. The emphasis on high-quality service for tourism and local businesses also contributes to higher consumer expenditure.
4th British Virgin Islands $1149.3
The British Virgin Islands, known for its offshore financial services and yachting tourism, experiences high per capita communication costs for reasons consistent with its island peers. The necessity of supporting a thriving international business sector and catering to high-value tourism means a robust and often expensive telecom network. Limited competition in smaller markets and the logistical costs of maintaining infrastructure across multiple islands, coupled with importing all necessary equipment, contribute to these elevated annual expenditures.
5th Switzerland $1134.2
Switzerland, a highly developed and affluent European nation, demonstrates some of the highest per capita communication spending outside of island territories. This reflects a populace with high disposable income and a strong demand for premium, high-speed, and reliable telecommunication services. The country boasts a highly advanced digital infrastructure, including extensive fiber-optic networks and widespread 5G coverage, requiring significant ongoing investment. Swiss consumers often opt for comprehensive plans that include the latest technologies and extensive data allowances.
11th USA $952.3
The United States ranks 11th globally in per capita annual communication costs, signifying a substantial outlay by its citizens for telecom services. As a large, developed economy, the US has extensive and technologically advanced telecommunications infrastructure, supporting a high demand for mobile data, broadband internet, and various streaming and online services. While the market is competitive, the continuous investment in upgrading networks (e.g., 5G, fiber optics), coupled with a culture of high data consumption and adoption of diverse digital services, contributes to significant average spending per person.
| Rank | Name | Indicator | Subindicator |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | $ 1,750 | ||
2 | $ 1,625 | ||
3 | $ 1,166 | ||
4 | $ 1,149 | ||
5 | $ 1,134 | ||
6 | $ 1,126 | ||
7 | $ 1,122 | ||
8 | $ 1,034 | ||
9 | $ 994 | ||
10 | $ 977 | ||
11 | $ 952 | ||
12 | $ 864 | ||
13 | $ 838 | ||
14 | $ 819 | ||
15 | $ 806 | ||
16 | $ 786 | ||
17 | $ 784 | ||
18 | $ 758 | ||
19 | $ 744 | ||
20 | $ 728 |