This chart compares the GDP of Africa and Taiwan from 1980 to 2024. It illustrates the economic growth and changes in both regions over this period. Taiwan's significant economic growth is particularly notable, and the GDP differences among various African countries are also highlighted.
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is an economic indicator that represents the total value of all goods and services produced within a country or region over a specific period. It plays a crucial role in assessing the size and growth of an economy.
1980s
In 1980, Taiwan's GDP was $42.285 billion, South Africa's was $89.412 billion, Nigeria's was $68.606 billion, Algeria's was $45.957 billion, and Kenya's was $13.449 billion.
During this period, Taiwan experienced steady economic growth due to economic reforms and industrialization. In contrast, South Africa maintained economic growth through mining and resource development despite the apartheid regime. Nigeria and Algeria also grew their economies through oil resources. Kenya relied mainly on agriculture, with noticeable growth in the tourism industry.
1990s
In 1990, Taiwan's GDP was $166.622 billion, South Africa's was $126.027 billion, Nigeria's was $62.165 billion, Algeria's was $67.171 billion, and Kenya's was $16.219 billion.
Taiwan saw rapid growth due to the expansion of the tech industry and an export-driven economy. South Africa continued its growth through new economic policies following the end of apartheid. Nigeria faced economic instability due to fluctuating oil prices but remained supported by its vital oil resource. Algeria sustained its economy through the growth of the oil and gas industry. Kenya experienced growth through political stability, agriculture, and tourism industry development.
2000s
In 2000, Taiwan's GDP was $330.680 billion, South Africa's was $151.855 billion, Nigeria's was $67.824 billion, Algeria's was $59.418 billion, and Kenya's was $18.206 billion.
Taiwan's explosive growth in the IT industry significantly boosted its economy. South Africa grew through a stable political environment and diverse economic policies. Nigeria continued to rely on its oil-based economic structure, while Algeria also focused on resource industries. Kenya's primary growth drivers were agriculture and the tourism industry.
2010s
In 2010, Taiwan's GDP was $444.281 billion, South Africa's was $417.315 billion, Nigeria's was $369.062 billion, Algeria's was $177.785 billion.
Taiwan maintained its position as a critical player in the global economy, achieving continuous growth. South Africa continued its economic growth through resource development and various industrial policies. Nigeria diversified its economy by nurturing multiple industries beyond oil. Algeria's economy remained resource-centric.
2020s
In 2020, Taiwan's GDP was $673.178 billion, South Africa's was $338.193 billion, Nigeria's was $429.423 billion, Algeria's was $164.774 billion, and Kenya's was $100.912 billion.
Taiwan continued its economic growth centered on the tech industry despite the COVID-19 pandemic. South Africa faced economic challenges due to the pandemic but gradually recovered through the resource industry. Nigeria dealt with fluctuating oil prices and the pandemic's impact, implementing various policies for economic recovery. Algeria also faced economic challenges due to the pandemic but sustained its economy through the resource industry. Kenya achieved economic growth through the recovery of the tourism industry and agricultural development.
Taiwan has experienced consistent economic growth since the 1980s, achieving a higher GDP than major African countries by the 2020s. South Africa, Nigeria, Algeria, and Kenya also grew based on their resources and industries but showed differences in economic structure and growth rates compared to Taiwan. These differences can be attributed to each country's economic policies, resources, industrial structure, and political stability.
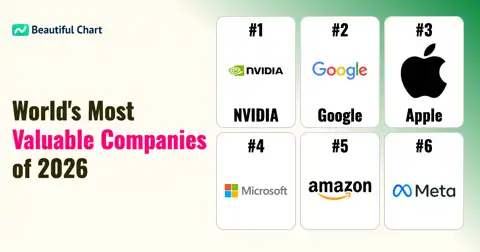
| Rank | Name | Indicator |
|---|---|---|
1 | $ 802B 958M | |
2 | $ 373B 233M | |
3 | $ 347B 594M | |
4 | $ 266B 779M | |
5 | $ 252B 738M | |
6 | $ 205B 130M | |
7 | $ 152B 377M | |
8 | $ 104B 1M | |
9 | $ 92B 123M | |
10 | $ 86B 911M | |
11 | $ 79B 605M | |
12 | $ 75B 244M | |
13 | $ 73B 761M | |
14 | $ 56B 310M | |
15 | $ 54B 708M | |
16 | $ 53B 205M | |
17 | $ 48B 221M | |
18 | $ 35B 450M | |
19 | $ 34B 405M | |
20 | $ 29B 872M |